Athletic Recovery Cryotherapy
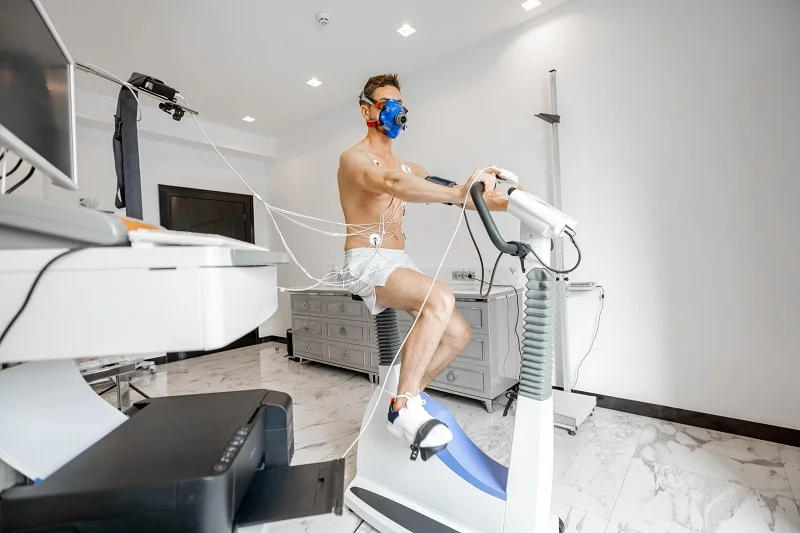
Athletes can use cryotherapy, cold water immersion, or ice baths as passive recovery methods during physical training. Professional rugby players often use cryostimulation exposure as part of their physical therapy to prevent injuries during training camps. The treatment involves exposing the athlete’s body to extremely low temperatures, ranging from -110°C to -140°C, for a short period, usually between 2-4 minutes.
The benefits of cryotherapy include reducing inflammation, improving circulation, vascular endothelial growth factor, and decreasing muscle soreness. Whole-body cryostimulation, cryostimulation exposure, cold baths, and cold water immersion can enhance the immune system and increase the production of endorphins, which are natural painkillers.
Cryotherapy, including whole-body cryostimulation and cryostimulation exposure, is particularly effective for exercise recovery after resistance or high-intensity interval training (HIIT) sessions. These workouts cause micro-tears in muscles, which lead to inflammation and soreness. Cold water immersion and cryotherapy help reduce this inflammation by constricting blood vessels and slowing down metabolic activity in the affected area.
Before undergoing whole-body cryostimulation or cold water immersion treatment, an intake session with a therapist must determine any injuries, health risks, or contraindications that may prevent athletes from receiving the therapy, especially after intense training.
Benefits of Cryotherapy for Athletic Recovery
Cold compression therapy, also known as cryotherapy or cryostimulation, has been gaining popularity among athletes for its beneficial effects on athletic recovery after intense training. This treatment involves exposing the body to extremely low temperatures through cooling or refrigeration for a short period. Cryotherapy can positively impact muscle soreness and inflammation, improve blood circulation, and reduce recovery time.
Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness
One of the primary benefits of cryotherapy, specifically whole-body cryostimulation, is its ability to reduce muscle soreness and inflammation. When athletes undergo intense physical activity, their muscles become damaged and inflamed, which can lead to injuries. However, cooling through refrigeration therapy can help alleviate these inflammatory symptoms by reducing swelling and promoting healing.
Another positive effect of cryotherapy is improved blood circulation. Cryostimulation during physical training can be achieved by cooling the body using cold stress exposure. When exposed, the body’s natural response is to increase blood flow to warm vital organs. As a result, more oxygen and nutrients are delivered to the muscles and other tissues that need it most, making cryotherapy an effective tool for resistance training. This increased blood flow can help speed up sports recovery after a workout or competition.
Research Supporting Cold Therapy
Research studies have supported the positive effects of cryotherapy on muscle healing and athletic recovery. One study found that whole-body cryotherapy effectively reduced muscle soreness and improved functional performance in rugby players after strenuous exercise (1). Another study showed that local cryotherapy effectively reduced pain and inflammation in patients with knee osteoarthritis (2). Cryostimulation, cold water immersion, and cooling have also benefited athletic recovery. Resistance training can also benefit from the use of these techniques.
Why Athletes Use Cryotherapy
Athletes use cryotherapy, specifically whole-body cryostimulation, to enhance their athletic performance by improving recovery after training or competing. By reducing muscle soreness and inflammation through cooling, improving blood circulation, and speeding up recovery time with cold water, athletes can train harder and more frequently without risking injury or burnout in sports.
Effectiveness of Cryotherapy for Muscle Recovery After Exercise
Reducing Muscle Soreness with Cold Water Immersion after Exercise
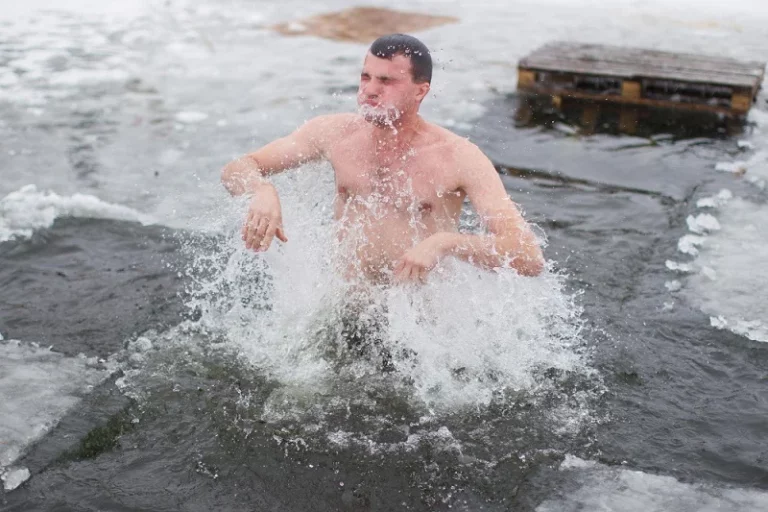
Cryotherapy, also known as cryostimulation, is a widespread technique in athletic recovery to reduce muscle soreness after physical exercise. This treatment involves exposing the body to extremely low temperatures, typically achieved through cooling with cold water or exposure to temperatures between -100°C and -140°C for a short period. The aim is to decrease inflammation and promote healing by constricting blood vessels and reducing blood flow to the affected area, which can be particularly helpful after resistance training.
Research has shown that cryotherapy, including cryostimulation and cooling, can effectively reduce muscle soreness after exercise. Several studies have demonstrated the benefits of cold therapy, with one study finding that participants who received cryotherapy treatment after performing eccentric exercise experienced less muscle soreness than those who did not. Another study showed that whole-body cryotherapy reduced exercise-induced muscle damage markers and improved perceived recovery in athletes following high-intensity training sessions. These studies highlight the potential benefits of cold therapies for post-exercise recovery.
Improving Muscle Recovery and Performance with Cryotherapy
In addition to reducing muscle soreness, whole-body cryostimulation can significantly improve muscle recovery and performance after resistance training. A study on soccer players demonstrated that those who received cooling treatments had better vertical jump height, sprint times, and lower perceived fatigue than those who did not receive cold treatment.
Furthermore, cryotherapy, also known as cryostimulation, uses cooling effects to reduce muscle damage associated with exercise therapy. This is achieved by applying cold temperatures to the affected area, which helps to constrict blood vessels and reduce inflammation. Cryotherapy can also provide analgesic effects that can provide effective pain relief and discomfort through the release of endorphins, making it an attractive non-invasive option for athletes recovering from injuries or intense workouts.
Stimulating Skeletal Muscle Strength with Cryotherapy
Another benefit of cryotherapy is its ability to stimulate skeletal muscle strength through cold exposure. A study on healthy young men found that whole-body cryostimulation improved isokinetic muscle strength in knee extensors after one session, making it a valuable addition to exercise and training routines. This suggests that regular use of cooling through cryostimulation could lead to significant improvements in muscular strength over time.
Potential Impact of Cryotherapy on Sports Performance
Cryotherapy, specifically cryostimulation, has been gaining popularity in sports as a potential way to improve performance through cooling. Studies have shown that cold therapy may positively affect athletes’ neuromuscular, aerobic, physical, and strength performance in athletes during exercise and training. Let’s take a closer look at how cryotherapy can influence an athlete’s results.
Cryostimulation for Neuromuscular Performance
Neuromuscular performance refers to the communication between the nervous system and muscles. Cryostimulation, a form of cooling therapy, involves exposing the body to extremely low temperatures (-110°C to -196°C) for a short period (usually 2-3 minutes). This process stimulates the nervous system and increases muscle activation during training. A study published in the Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research found that using cryostimulation before exercise improved neuromuscular performance in male rugby players. The players could generate more power during sprinting exercises after being exposed to cold physical cooling therapy.
Improving Aerobic and Physical Performance
Aerobic capacity and physical endurance are crucial components of many sports. Cryotherapy, also known as cryostimulation or cold therapy, has improved both of these areas in athletes during training and performance. In a study published in the International Journal of Sports Medicine, researchers found that exposing runners to whole-body cryotherapy sessions twice a week for three weeks significantly improved running economy and VO2 max. Another study on soccer players found that those who received daily whole-body cryotherapy sessions had better physical recovery than those who did not receive any treatment.
Decreasing Muscle Soreness and Improving Strength Performance
Muscle soreness is often experienced by athletes after intense exercise or competition. Cryotherapy, also known as cryostimulation, using cold temperatures may help alleviate this soreness by reducing inflammation and promoting faster recovery times. A study published in The Journal of Sports Medicine and Physical Fitness found that tennis players who underwent post-match whole-body cryotherapy sessions experienced less muscle soreness and improved strength performance due to the effects of cold treatment compared to those who did not receive any treatment.
Standardized Protocol for whole-body Cryotherapy (WBC)
Whole-body cryotherapy (WBC) or cryostimulation is a popular treatment among athletes and fitness enthusiasts due to its many benefits, including reduced inflammation, improved muscle recovery, and increased energy levels. However, it is crucial to have a standardized protocol to ensure the safety and effectiveness of cold therapy. Here are some key points to keep in mind when undergoing WBC or PBC (partial body cryotherapy), or RBC (local cryotherapy)
WBC Sessions:
Typically, whole-body cryotherapy (also known as whole-body cryostimulation) sessions for cold compression therapy last between 2-4 minutes, with a recommended frequency of 1-2 sessions per day for optimal results. It’s important not to exceed these guidelines as overexposure can lead to adverse side effects such as frostbite or skin irritation. Taking a few days off between sessions is also advisable to allow your body to recover.
Hematological Parameters:
Studies have shown that WBC exposure can positively affect hematological parameters such as increased red blood cell count and hemoglobin concentration, improving oxygen delivery throughout the body. These effects can particularly benefit individuals undergoing exercise or physical therapy, as they may experience strength and overall physical performance.
Temperature Range:
A systematic review of WBC protocols found that whole-body cryostimulation and whole-body cryotherapy using a temperature range of -110°C to -140°C was the most effective treatment for achieving desired physiological responses. This cold compression therapy provides optimal stimulation without causing any harm or discomfort.
Efficiency:
Compared to traditional ice baths or water immersion, WBC offers a more efficient and comfortable way to achieve whole-body cryostimulation. With WBC, you only need a few minutes of exposure compared to the longer duration required for ice baths or water immersion. WBC is a viable option for those seeking cold compression therapy, exercise therapy, or treatment with PBC.
Risks and Benefits of Exposing Your Body to Subzero Temperatures
Cold exposure through whole-body cryotherapy and cryostimulation is every day in exercise and training for fitness and recovery, but it comes with risks and benefits. Exposure to extreme cold temperatures can have benefits such as reducing inflammation and promoting muscle recovery. However, whole-body cryotherapy and cryostimulation can lead to acute effects such as vasoconstriction and increased heart rate.
Benefits of Cold Exposure
One of the most significant benefits of cold exposure is its ability to reduce inflammation. When the body experiences an injury or intense workout during exercise training, inflammation is part of the natural healing process. This inflammation can be beneficial in small amounts but can become detrimental when excessive. Cryostimulation effects through cold exposure have been shown to reduce tumor necrosis factor by constricting blood vessels and decreasing blood flow to affected areas.
Another benefit of cold exposure is its ability to promote muscle recovery after exercise or training. Cryostimulation and cold baths are standard methods used in fitness for cooling down the body’s skin temperature, which helps reduce the effects of muscle soreness caused by microtears in the tissue.
Risks of Cold Exposure
While many benefits are associated with cold exposure, risks are also involved. Cryostimulation, a freezing treatment used in exercise, can lead to various effects on the body. Exposure to freezing temperatures can cause vasoconstriction, narrowing blood vessels that reduce blood flow throughout the body. This effect can lead to increased heart rate and changes in systolic blood pressure levels.
Prolonged exposure to cold temperatures can result in hypothermia or frostbite if not appropriately managed. Cold exposure can harm the body, but cryostimulation can be an effective treatment. Hypothermia occurs when core body temperature drops below normal levels, leading to shivering, confusion, and lethargy symptoms.
The Importance of Athletic Recovery Cryotherapy
Athletic recovery cryotherapy, or whole-body cryostimulation, is essential to sports performance. It helps physically active subjects recover from intense workouts and training, reduces muscle soreness and inflammation caused by exercise, and enhances overall recovery time through cold temperatures. Cryotherapy has been scientifically proven to be an effective method for promoting athletic recovery, making it a popular choice among athletes worldwide.
Cryotherapy, also known as cryostimulation, is a popular technique used during exercise training to enhance the effects of physical activity. By exposing the body to subzero temperatures for a short period, cryotherapy triggers the body’s natural healing response, promoting faster recovery times and improved muscle oxygenation. Liquid nitrogen is used to cool the air around the athlete, creating a cold environment that stimulates blood flow and maximizes the benefits of training.
One of the significant benefits of whole-body cryostimulation as a cold treatment is its ability to reduce muscle soreness and inflammation after exercise. After intense workouts or competitions, muscles can become swollen and inflamed due to micro-tears in the muscle fibers. Cryotherapy helps to reduce this inflammation by constricting blood vessels in the affected area, limiting swelling and pain.
Another essential benefit of athletic recovery cryotherapy treatment is its potential impact on sports performance. By reducing muscle soreness and inflammation through whole-body cryostimulation, athletes can train harder and longer without experiencing fatigue or injury caused by the cold. These effects of increased training capacity can lead to better performance during competitions and games.
To ensure maximum benefits from athletic recovery cryotherapy treatment, it is imperative to follow the proper protocol. This protocol includes specific cold temperature exposure time, clothing requirements, post-cryotherapy activities, and more. It is especially beneficial after intense exercise.
While there are risks associated with exposing your body to subzero temperatures during cryotherapy sessions, such as frostbite or hypothermia if proper precautions are not taken into consideration, these effects are minimal when compared to the many benefits of cryostimulation and the positive cold exposure that this treatment method provides.